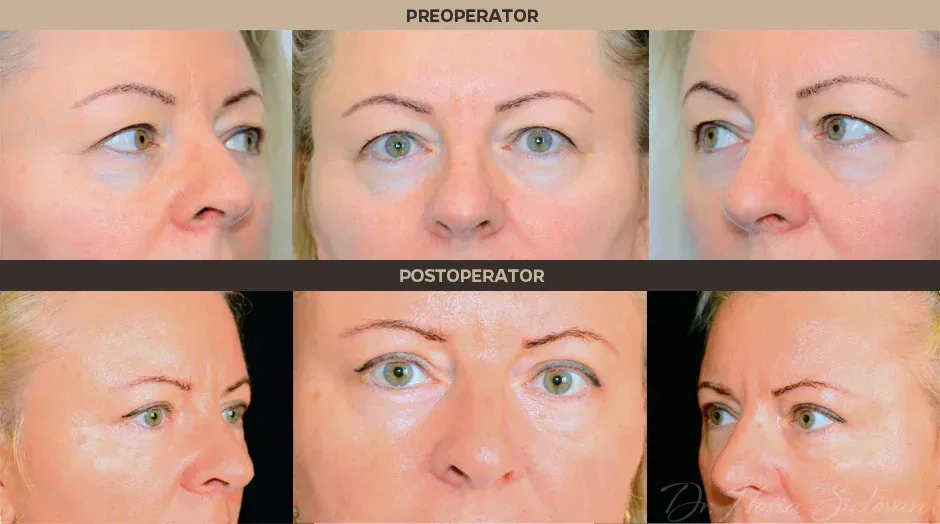
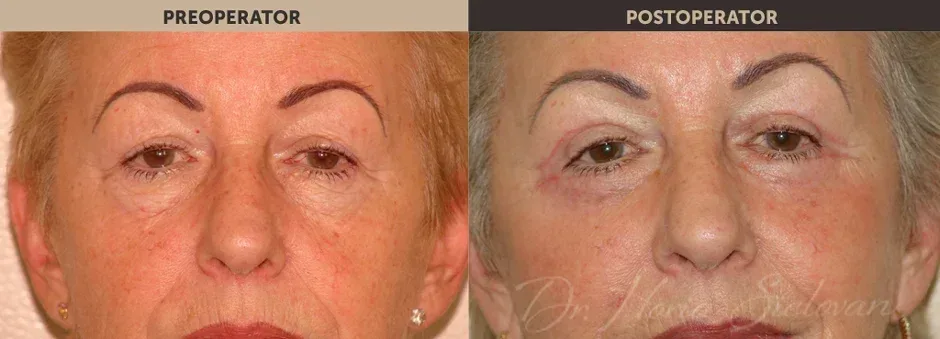
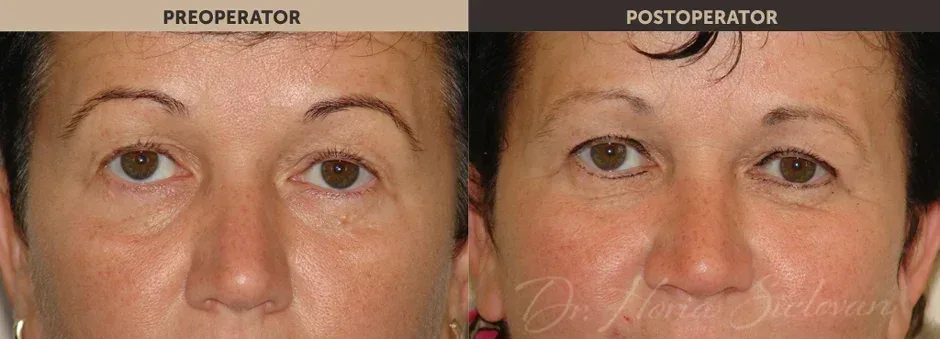
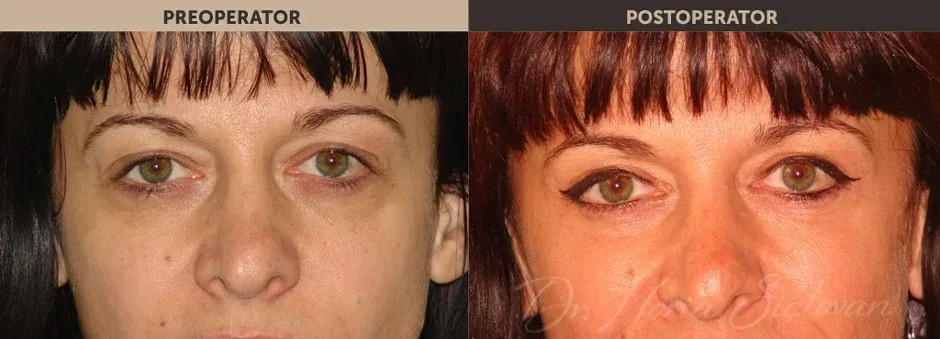
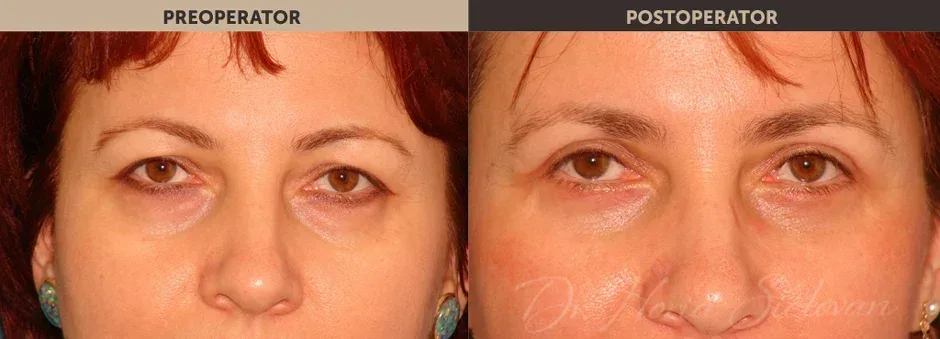
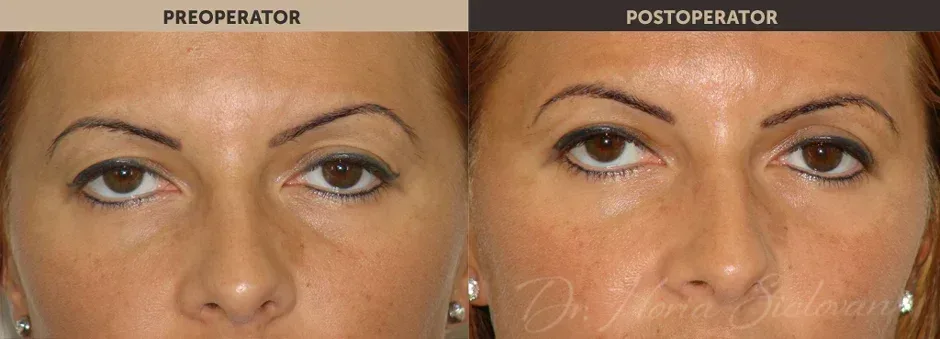
Purpose of the Procedure
Blepharoplasty is a surgical procedure that improves the appearance of the eyelids by treating:
- Excess skin that creates folds and deforms or masks the natural contour of the upper eyelid, sometimes affecting normal vision
- Excess adipose tissue (fat deposits) in the upper and lower eyelids
- Excess skin in the lower eyelid (“under-eye bags”)
Surgical Procedure
Correction of excess skin and fat is performed surgically through blepharoplasty, improving the tired and aged appearance of the eyes. The procedure may include:
- Correction of periorbital wrinkles (“crow’s feet”) through partial myomectomy of the orbicular muscle
- Association with other facial rejuvenation procedures: facelift and cosmetic eyebrow surgery
Incisions are hidden in the natural folds of the eyelids, with scars being almost invisible postoperatively.
Recovery
- Application of ointments or ophthalmic drops and cold compresses
- Edema, bruising, burning sensation or “dry eyes” – normal postoperatively, controlled with medication
- Resumption of daily activities: a few days postoperatively
- Removal of sutures: 5–7 days
- Edema gradually decreases, scars fade within a few weeks
- Wearing sunglasses during the recovery period is recommended
Risks
- Bleeding, incision infections, poor healing
- Temporary visual disturbances (“blurred vision”), local discomfort (“dry eyes”)
- Ectropion or pulling of the lower eyelid – rare, usually temporary
- Risks associated with anesthesia
Results
- The result appears gradually as edema and bruising disappear
- Younger appearance of the eyelids and surrounding area
- Final result: a few weeks, scars become almost invisible after several months (up to one year)
- The durability of results depends on the physiological aging process of each person